OpenTelemetry
OpenTelemetry support is currently only available for the Python SDK.
Hatchet supports exporting traces from your tasks to an OpenTelemetry Collector to improve visibility into your Hatchet tasks.
Usage
Setup
Hatchet’s SDK provides an instrumentor that auto-instruments Hatchet code if you opt in. Setup is straightforward:
First, install the otel extra with (e.g.) pip install hatchet-sdk[otel]. Then, import the instrumentor:
You bring your own trace provider and plug it into the HatchetInstrumentor, call instrument, and that’s it!
Check out the OpenTelemetry documentation for more information on how to set up a trace provider.
Spans
By default, Hatchet creates spans at the following points in the lifecycle of a task run:
- When a trigger is run on the client side, e.g.
run()orpush()is called. - When a worker handles a task event, such as starting to run the task or cancelling the task
In addition, you’ll get a handful of attributes set (prefixed by hatchet.) on the task run events, such as the task name and the worker ID, as well as success/failure states, and so on.
Some other important notes:
- The instrumentor will automatically propagate the trace context between task runs, so if you spawn a task from another task, the child will correctly show up as a child of its parent in the trace waterfall.
- You can exclude specific attributes from being attached to spans by providing the
otelconfiguration option on theClientConfigand passing a list ofexcluded_attributes, which come from this list.
Integrations
Hatchet’s instrumentor is easy to integrate with a number of third-party tracing tools.
Langfuse
For example, you might be interested in using Langfuse for tracing an LLM-intensive application.
Note that this example uses Langfuse’s V3 (OTel-based) SDK. See their docs for more information.
First, configure the Langfuse client as described by their documentation:
Langfuse will set the global tracer provider, so you don’t have to do it manually.
Next, create an OpenAI client using Langfuse’s OpenAI wrapper langfuse.openai as a drop-in replacement for the default OpenAI client:
And that’s it! Now you’re ready to instrument your Hatchet workers with Langfuse. For example, create a task like this:
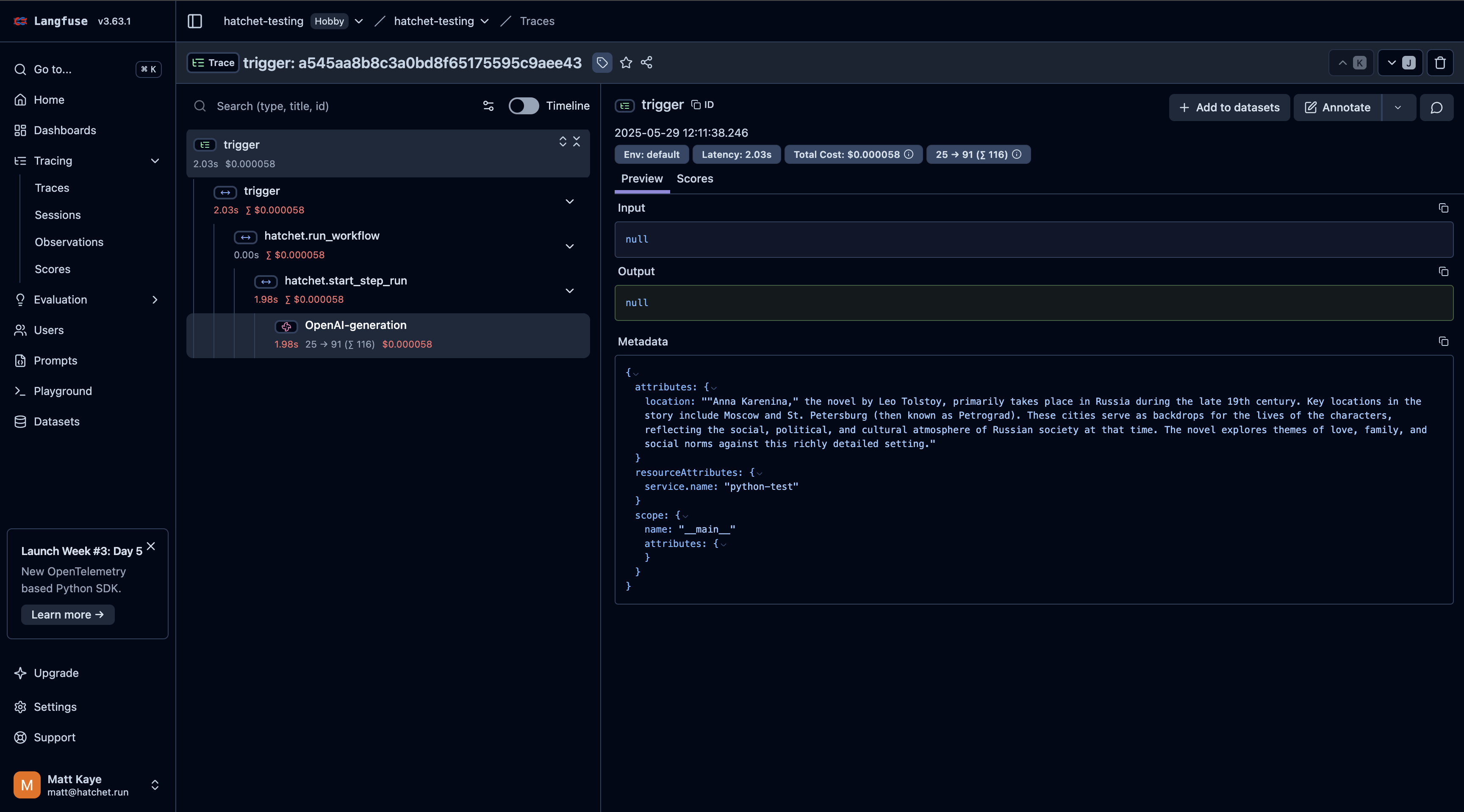
And finally, run the task to view the Langfuse traces (cost, usage, etc.) interspersed with Hatchet’s traces, in addition to any other traces you may have:
When you run this task, you’ll see a trace like this in Langfuse!